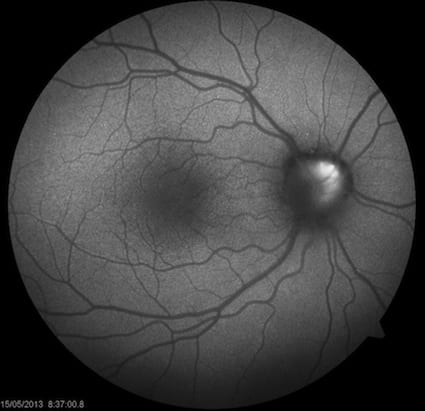
Autofluorescence is a physical phenomenon whereby a substance which has a light shone onto it emits light of a different wavelength. This occurs in several biological tissues (such as the retinal pigment epithelium), and several non-biological tissues (such as US banknotes - to prevent counterfeiting).
Retinal Autofluorescence is a complimentary test to clinical examination and retinal angiography. It gives us specific information about the health of the retinal pigment epithelium. It also allows us to detect other substances within the retina, such as lipofuscin.
Retinal autofluorescence is most helpful in monitoring the progression of slowly progressive diseases of the retinal pigment epithelium, such as dry macular degeneration and rare autoimmune chorioretinopathies (such as serpiginous chorioretinopathy).
A normal retinal autofluorescence picture is shown below.
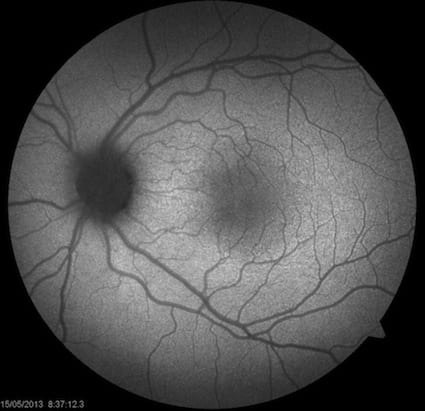
This is an uncommon disease in which diabetes is linked to hearing abnormalities. It follows inheritance pattern down the maternal lines.
Rather than these patients showing signs of diabetic retinopathy in their eyes, they also show abnormalities of the retinal pigment
epithelium, that can appear very similar to dry macular degeneration.
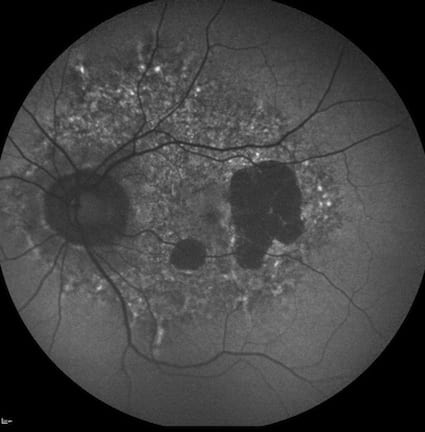
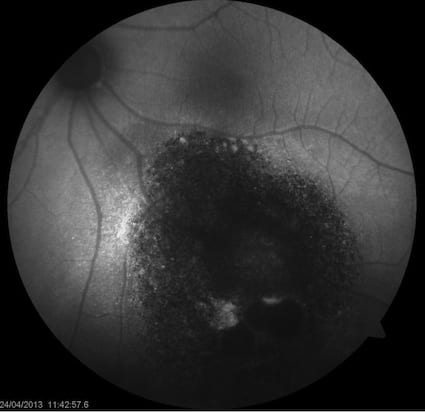
Thankfully, choroidal melanoma is a rare disease. Sometimes it can be difficult to differentiate from a choroidal naevus (which is
harmless). Melanomas frequently produce a substance called lipofuscin, which autofluoresces. This can be picked up by autofluorescence
photography as a white/bright spot on the retina. Below is a retinal photograph of a choroidal melanoma, and below that, the corresponding
autofluorescence photograph.
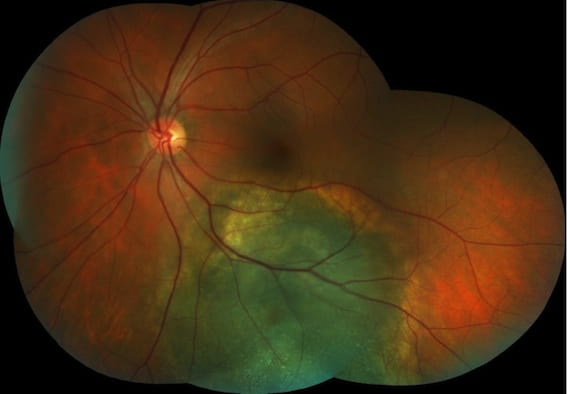
Swollen optic nerves can be a sign of serious diseases of the brain and central nervous system (such as raised intracranial pressure or
multiple sclerosis). Sometimes, it can be due to less worrying diseases such as optic disc drusen. These are abnormal accumulations of waste
products within the optic nerve head. These drusen are sometimes visible on autofluorescence photography of the retina and optic nerve.